
一种倒置的微流控装置,用来研究不同的氧环境和水凝胶组成对3D内皮细胞网络形成的影响。
Introduction
3D内皮细胞网络的形成是在血管生成、内皮细胞分化和原始血管形成中的基本生物过程,在多种生理和病理发展中均有参与。例如,肿瘤可以通过血管生成过程,从循环细胞中形成血管来获得血液供应。在体内内皮细胞网络的形成受到多种微环境因素的影响包括氧张力、生长因子、细胞因子和周围组织成分。
在众多因素中,氧在许多重要过程中发挥巨大作用,刺激不同的细胞行为,进而影响体内的各种生物活动。为了在体外研究氧的作用,不同氧张力的氧条件的定义被建立:
- 常氧(Normoxia)通常用于描述氧气等级在接近大气环境(≈20% O2 5% CO2)。
- 缺氧(Hypoxia)被认为是氧张力低于常氧,有以下两种缺氧水平:
- 生理性缺氧,被认为是适合于组织和细胞生长的氧微环境,大约为5% O2。
- 病理性缺氧,疾病状态下组织和细胞周围的低氧微环境,通常为1% O2或更低。
此外,不同生物体内不同氧张力所形成的氧梯度,以及细胞和组织中氧张力的变化,被认为是影响生物功能的潜在刺激因子。
研究表明,氧张力在Vasculogenesis和Angiogenesis过程中都起着至关重要的作用,可以极大地影响内皮细胞的血管形成。在体内,氧梯度是由位于组织中的不同氧张力建立起来的,梯度已被认为是激活各种生物功能的潜在线索。然而,由于技术上的挑战和限制,很少有研究集中在研究氧梯度下的细胞反应。
注意:Vasculogenesis和Angiogenesis是有区别的,大致上可以认为前者是由内皮细胞变成血管,后者则是从已有血管形成新血管。
此外,在内皮细胞的3D网络形成的过程中,细胞外基质(ECM)同样是调节细胞生长、分化和迁移的关键因素。大量水凝胶材料,如胶原、纤维蛋白原、明胶和透明质酸(HA)被用于构建体外ECM模型。由于技术限制,当前研究细胞行为的体外模型通常受限于单个因子,而没有空间变化。
当前已有不少可以控制微环境如氧张力的细胞培养微流控装置被开发。然而利用气体控制氧张力往往会在细胞培养基中产生气泡,这可能会在细胞培养通道中引起不希望的剪切力和培养基的蒸发。直接化学添加提供了一个简单的解决方案。然而,培养基组成的改变可能在细胞培养中产生额外的人工产物。此外,现有微流控细胞培养器件的多层封闭通道设计,往往使器件中的水凝胶细胞培养和进一步的3D成像难以实现,限制了器件的实际应用。
在本装置中,使用带有氧气控制器的传统细胞培养箱来控制整体氧气张力,而氧气梯度是基于先前开发的空间受限的化学反应方法产生的。本网络形成实验运行在5个不同氧微环境,包括:3个均匀的氧张力(常氧、5%和1%)和2个氧梯度环境(常氧和5%)。实际的在常氧和5% O2下的氧梯度通过宽场荧光寿命成像显微镜(widefield frequency domain fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy, FD-FLIM)测量,氧敏感性的染料用于表征水凝胶样品内部的3D氧张力曲线。为了进一步研究氧气微环境和ECM成分对网络形成的综合影响,利用具有生长因子(碱性成纤维细胞生长因子bFGF和血管内皮生长因子VEGF)的纤维蛋白原基水凝胶和三种不同的HA浓度来构建用于3D细胞培养的ECM。
Figure 1
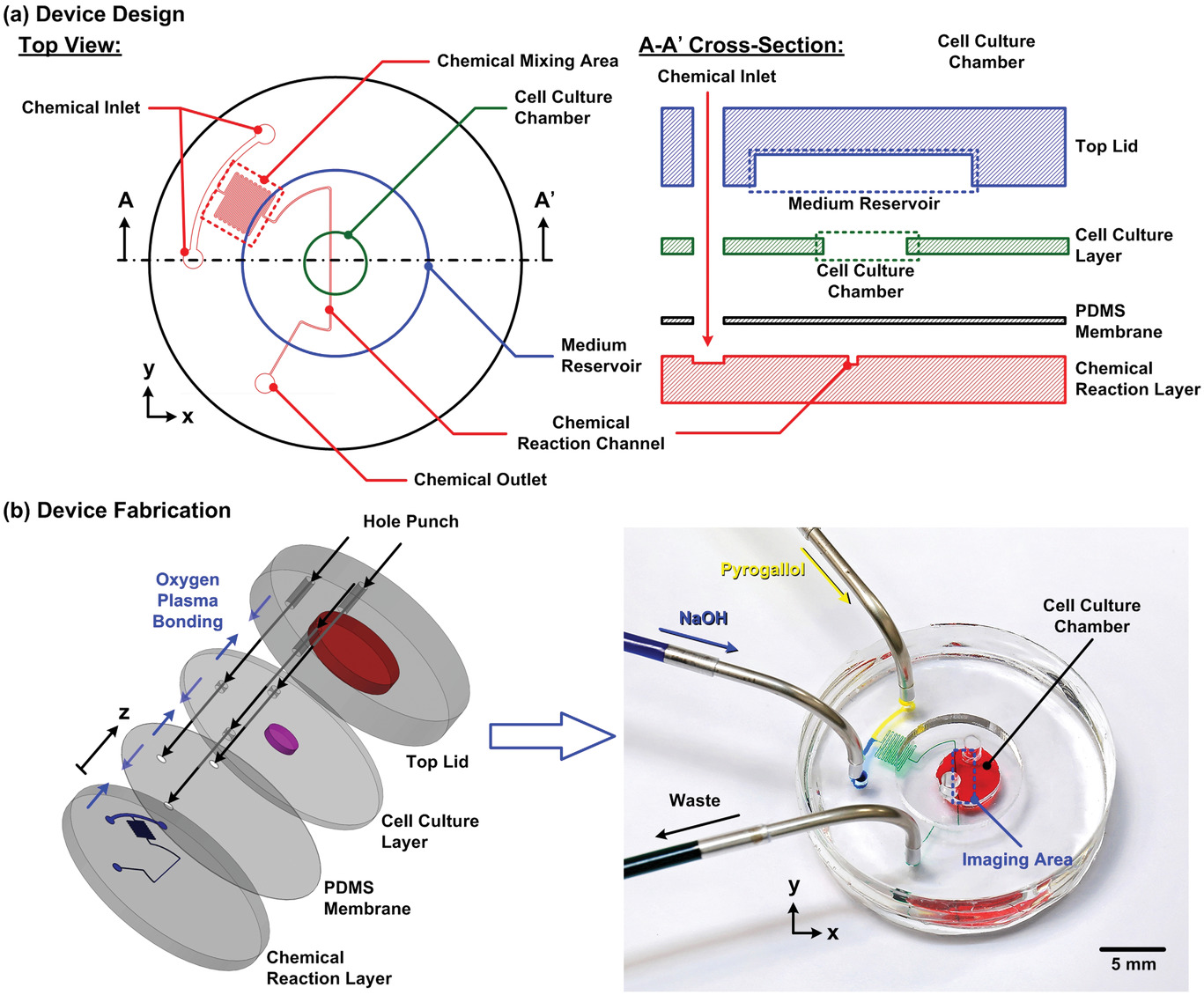
- (a)倒置微流控装置的示意图(俯视图和横截面图),用于可控的氧气微环境下在水凝胶中进行细胞培养实验。该装置由四个PDMS层构成:
- 底层设计了一套化学反应微流控通道,有两个入口和一个出口,用于氧清除化学反应。
- 在化学反应层的上面是一层厚度为30 μm的PDMS薄膜,以防止氧清除化学反应的化学物质与细胞直接接触,同时保持不同层之间氧气的有效运输。
- 在膜的上面放置了一个1 mm厚的细胞培养层,上面有一个圆形的细胞培养室,细胞-水凝胶混合物在其中进行培养。
- 整个装置的最上层是一个覆盖细胞培养室的顶盖,作为培养基的储存器,并防止培养基蒸发和周围环境的污染。
- (b)装置制造过程和制造好的微流控装置的实验照片。
Figure 2

- (a)不同氧微环境下细胞培养实验的实验装置和工艺流程。氧张力被2个方法控制:
- 均匀的不同等级(常氧、5%和1%)的氧张力通过细胞培养箱的氧张力控制单元而控制。
- 装置中的氧梯度通过先前开发的细胞培养箱的空间限制化学反应方法来生成。
- (b)图像分析过程和图像分析参数定义。首先将一堆共聚焦图像投影到单个2D最大密度投影图像上,然后使用计算机代码识别细胞网络。网络长度和方向基于识别的网络来计算。
Pyrogallol即邻苯三酚/焦性没食子酸,用于吸收氧气,具体原理见:其一、其二。

Figure 3
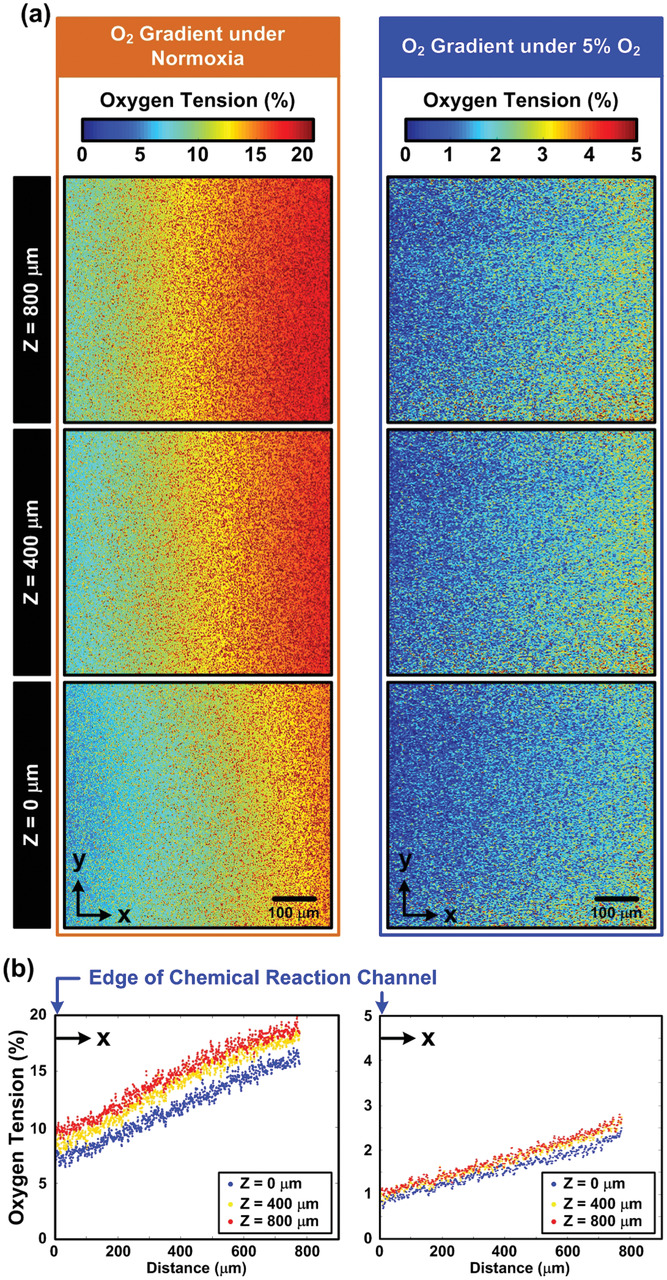
- (a)使用氧敏感荧光染料和宽场荧光寿命成像显微镜(FD-FLIM),在常氧和5% O2环境下,沿z轴不同高度(距水凝胶底部z分别为0、400和800 µm)测量水凝胶内2D氧张力曲线。
- (b)两种氧环境和不同高度下,水凝胶中氧张力沿x轴方向上的定量。
Figure 4
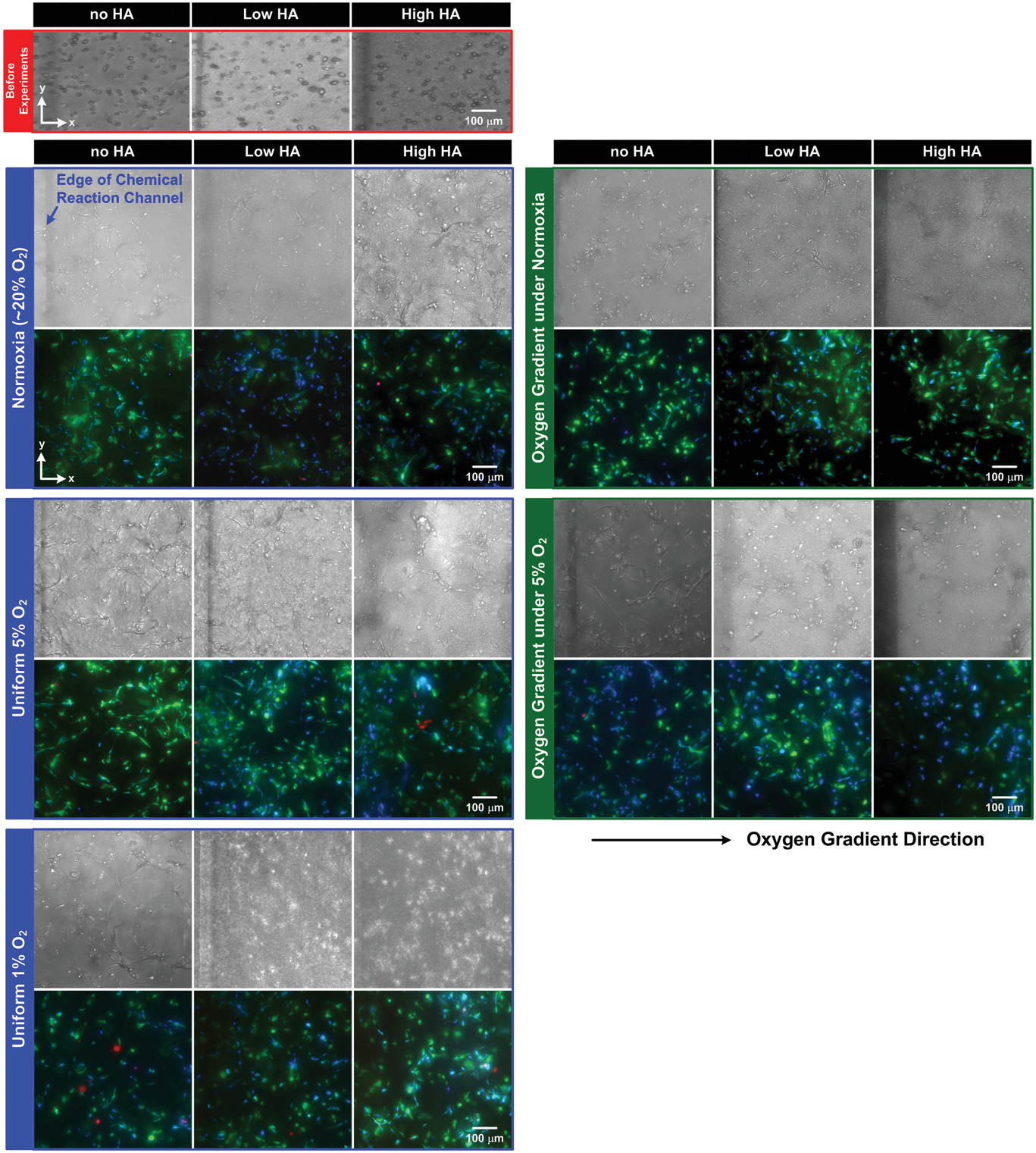
特定垂直位置上的HUVECs亮场和荧光图像。其中HUVECs培养在水凝胶中72 h,染色以用来进行活性分析(绿色:Calcein AM,活细胞/红色:Ethidium Homodimer-1,死细胞/蓝色:Hoechst,核)。分为培养前与培养在不同HA组分以及多种氧微环境等条件。
Figure 5

来自活/死荧光图像包括:a)细胞活性;b)细胞数目;c)不同培养条件下单细胞数量比的定量分析结果。
- (a)细胞活性的测量结果表明,除了在均匀5% O2条件下不含HA的水凝胶外,其他所有培养条件的细胞存活率均高于95%,证实了微流控装置和氧梯度生成方案下良好的细胞存活率。
- (b)与常氧条件相比,无HA水凝胶中5% O2培养的细胞数量略高,与添加HA水凝胶培养的细胞数量相似。然而,当O2浓度降低到1%时,细胞数量减少了50%以上。表明1%的低氧水平阻碍了不同成分水凝胶内的细胞增殖。在氧梯度条件下,细胞数显著增加,尤其是在添加了HA的情况下。
- (c)单细胞数量比的相关分析。
- 单细胞数量比反映3D网络形成,越低则代表水凝胶下更多的3D网络形成。相同水凝胶组成下,均匀5% O2条件下单细胞数量较低。无HA且缺氧条件下,这一比率增加巨大(超过100%),暗示水凝胶组成影响培养中水凝胶中细胞的缺氧响应。而作为对比,氧梯度条件下单细胞数量比低于常氧条件,暗示5%均匀氧张力和氧梯度的存在会促进培养在水凝胶中HUVECs的相互连接。
- 相同氧微环境下,研究水凝胶组成的影响。结果显示,添加HA将降低单细胞数量比。尤其是在1% O2条件下最为显著,并且,低HA添加量为最优配置。
Figure 6

- (a)不同HA组成和氧微环境下,由培养在水凝胶72 h、细胞骨架染色(红:F-肌动蛋白/蓝:核)的HUVECs共聚焦显微图像得到的最大密度投影图像。图像的底部行是顶部行图像中带有虚线框标记的区域的放大视图。
- (b)培养在均匀5% O2和梯度5% O2下的高HA水凝胶中的3D HUVECs网络的透视图。结果表明,在氧梯度条件下,HUVECs具有较长的管状结构和较高的网络密度。
- (c-d)由细胞骨架荧光图像定量分析网络长度和方向。对不同氧微环境下的实验结果与相同成分的水凝胶内的常氧(对照)实验结果进行了统计分析,结果显著区别于对照组。
- 没有HA的情况下,网络长度没有显著性差异。有HA的情况下,常氧条件下网络长度会减少。结果表明,在氧梯度微环境下,可能存在导致网络长度增加的不同机制。
- 氧梯度情况下,方向指数增加,暗示在水凝胶中培养时,HUVECs的形态在形成3D网络过程中沿着氧梯度伸长并对齐。证实了氧及其梯度在调控三D内皮细胞网络形成和形态中的重要作用。
Discussion
本文研制了一种用于细胞培养的倒置微流控细胞培养装置,用于在水凝胶中产生氧梯度。
- 提供了体外可控的氧张力微环境,用于模拟体内微环境,研究3D培养模型的细胞响应。
- 在3D培养环境下再一次确认了相似于生理性缺氧的均匀的5% O2微环境可以促进HUVECs增殖。
- 证明了常氧和缺氧(5% O2)环境的氧梯度可以促进HUVECs 3D网络的形成。且实验中形成的3D内皮网络具有倾向于沿氧梯度方向排列的方向性,特别是在添加HA的水凝胶中。
- 虽然已有多项研究发现,高分子HA具有抗血管生成的作用,但已经证实,重构良好的HA水凝胶能够增强血管生成过程。
Reference
Hsu H-H, Ko P-L, Wu H-M, et al. Study 3D Endothelial Cell Network Formation under Various Oxygen Microenvironment and Hydrogel Composition Combinations Using Upside-Down Microfluidic Devices[J]. Small, , n/a(n/a): 2006091.



